Introduction
After setting up Krill to issue ROA, the next step will be to announce them. I will be using BuyVM as they have no additional cost for BGP transit. You will need to contact support to get your ASN approved.
Adding ASN
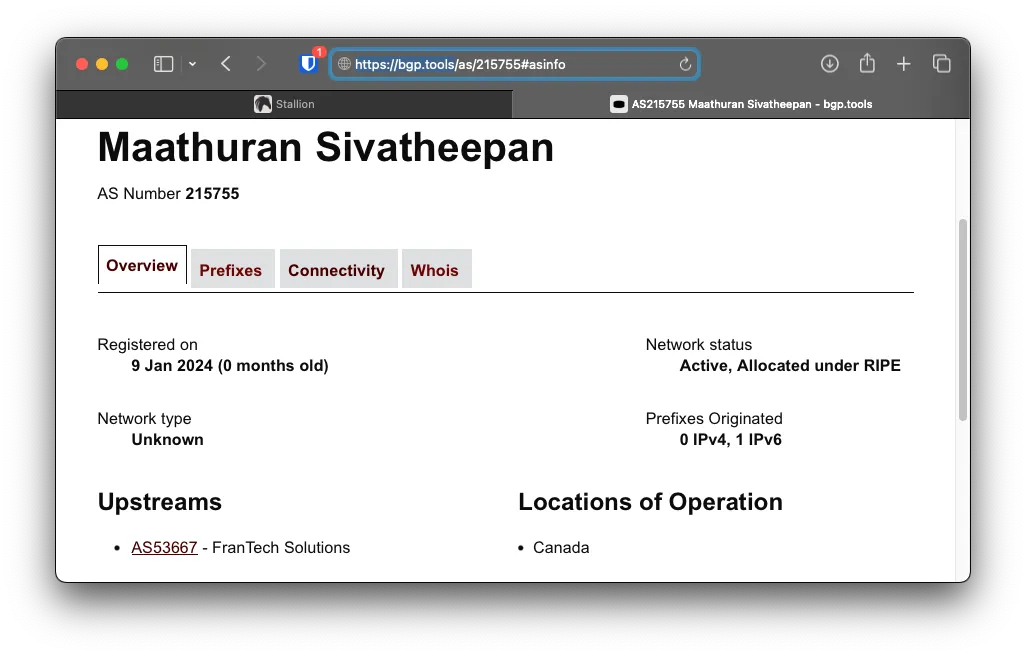
For ASN approval, contact support asking to add your ASN to your Stallion account, you will get sent a verification code to your RIPE Abuse contact. After it’s approved, it will look like this.
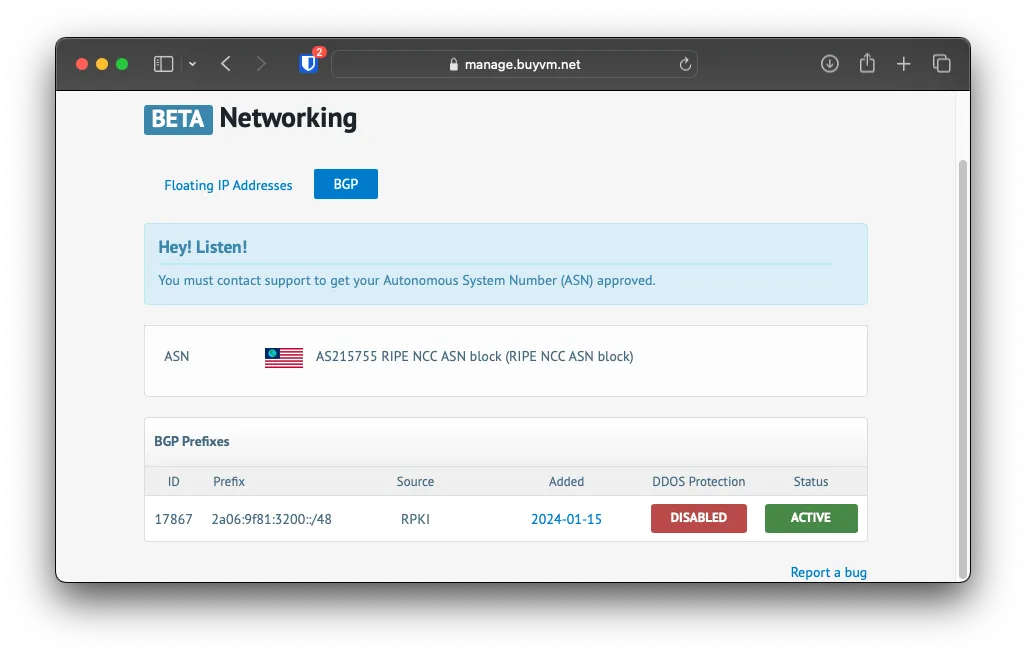
Assinging IPv6 Address
Make sure that you assign the VM an IPv6 Address first.
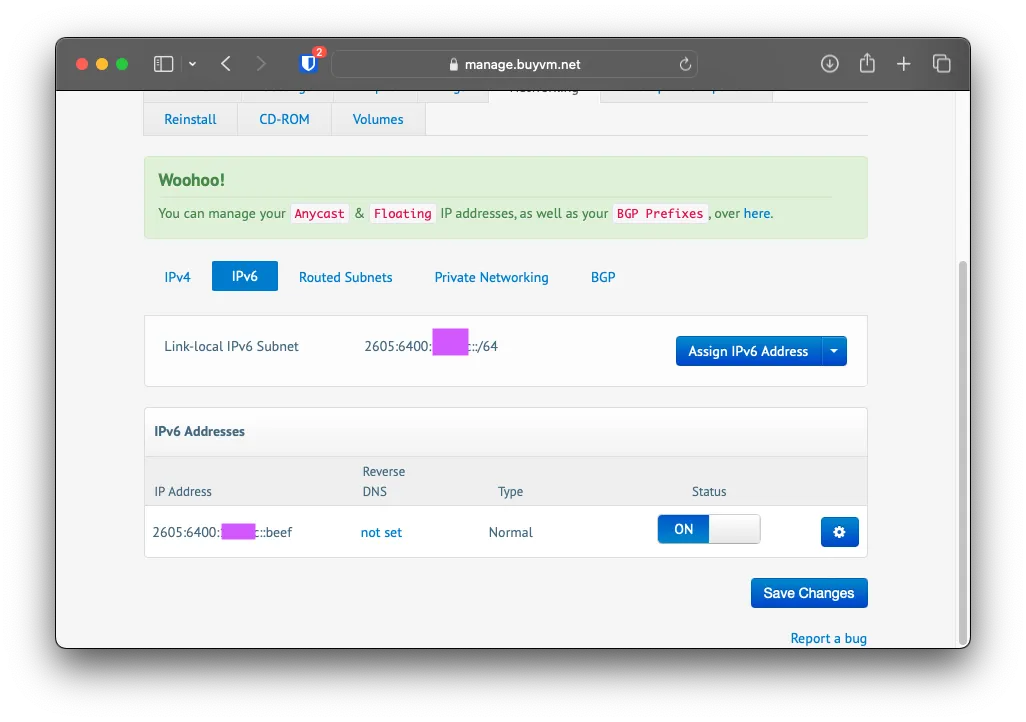
Configuring BGP Session
Under BGP, click Configure Session and select your IPv4/6 Address; keep the Connection Mode and BGP Table View with the default values. Then click on Save
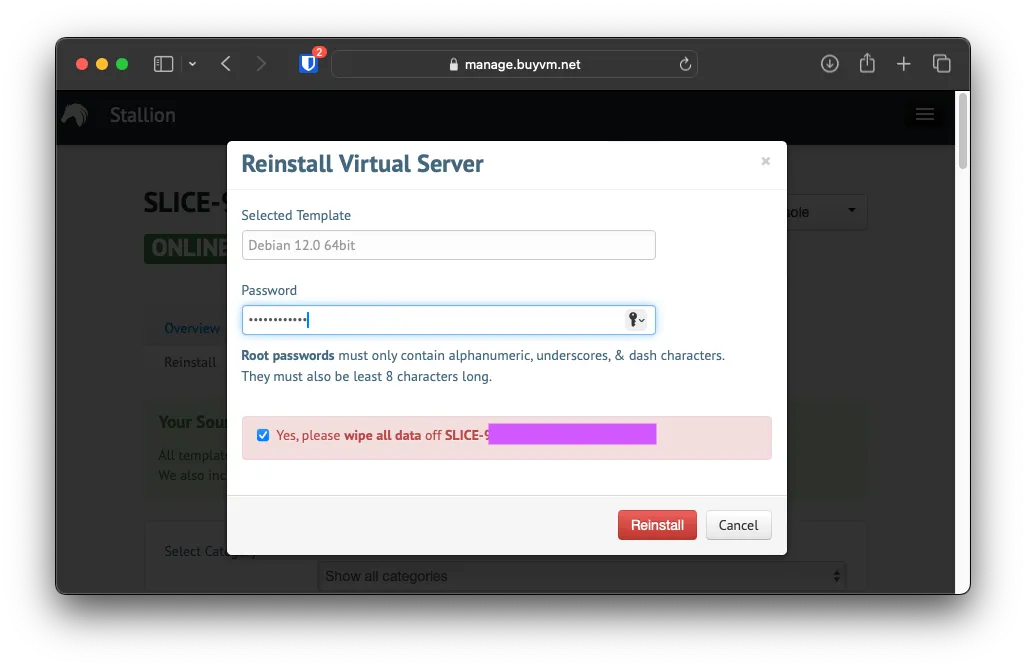
Reinstalling Debian 12
If you haven’t already, reinstall Debian 12 onto the VM, as we will be using Bird2 to set up the BGP route.
Updateing Debian 12
Use the web terminal to VNC into the VM, run the following to update and upgrade all the packages.
apt update
apt upgrade -yIf you are unable to SSH into the server, install openssh with the following apt install openssh-server
After that, remote into the server with ssh root@IPv4/6Address. You will be prompted with the following after login
Linux localhost 6.1.0-9-amd64 #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Debian 6.1.27-1 (2023-05-08) x86_64
The programs included with the Debian GNU/Linux system are free software;
the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the
individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright.
Debian GNU/Linux comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent
permitted by applicable law.
Last login: Wed Jan 16 17:38:40 2024
root@localhost:~# Adding static IPV4/6 Address
use nano to edit /etc/network/interfaces and change the file to the following. Make sure to fill out your IP’s
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
source /etc/network/interfaces.d/*
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
allow-hotplug eth0
iface eth0 inet static
address xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
dns-nameservers xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
iface eth0 inet6 static
address 2605:6400:10:xxxx::beef
netmask 48
gateway 2605:6400:10::1Save the file and restart the network service with systemctl restart networking. It might take a couple of seconds to connect to IPv6.
You can test it out by pinging Google with ping6
root@localhost:~# ping6 google.com
PING google.com(yyz12s08-in-x0e.1e100.net (2607:f8b0:400b:803::200e)) 56 data bytes
64 bytes from yyz12s08-in-x0e.1e100.net (2607:f8b0:400b:803::200e): icmp_seq=1 ttl=117 time=14.0 ms
64 bytes from yyz12s08-in-x0e.1e100.net (2607:f8b0:400b:803::200e): icmp_seq=2 ttl=117 time=13.2 ms
^C
--- google.com ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1002ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 13.196/13.611/14.026/0.415 msInstalling Bird2
On the console, install Bird2 with the following
apt install bird2 -yyou will see the following when installing
root@localhost:~# apt install bird2 -y
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
libssh-gcrypt-4
Suggested packages:
bird2-doc
The following NEW packages will be installed:
bird2 libssh-gcrypt-4
0 upgraded, 2 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 972 kB of archives.
After this operation, 2,242 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://security.debian.org/debian-security bookworm-security/main amd64 libssh-gcrypt-4 amd64 0.10.6-0+deb12u1 [219 kB]
Get:2 http://ftp.us.debian.org/debian bookworm/main amd64 bird2 amd64 2.0.12-7 [753 kB]
Fetched 972 kB in 0s (6,383 kB/s)
Selecting previously unselected package libssh-gcrypt-4:amd64.
(Reading database ... 26506 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../libssh-gcrypt-4_0.10.6-0+deb12u1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libssh-gcrypt-4:amd64 (0.10.6-0+deb12u1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package bird2.
Preparing to unpack .../bird2_2.0.12-7_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking bird2 (2.0.12-7) ...
Setting up libssh-gcrypt-4:amd64 (0.10.6-0+deb12u1) ...
Setting up bird2 (2.0.12-7) ...
Creating config file /etc/bird/bird.conf with new version
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/bird.service -> /lib/systemd/system/bird.service.
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.36-9+deb12u3) ...
root@localhost:~# Installing Pathvector
To make generating Bird configurations files easier and with a YAML config, we will be using Pathvector. Install it with the following commands on Debian 12.
apt install curl -y
curl https://repo.pathvector.io/pgp.asc > /usr/share/keyrings/pathvector.asc
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/pathvector.asc] https://repo.pathvector.io/apt/ stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pathvector.list
apt update && apt install -y pathvectorSetting up Pathvector config
use nano to make a new file called pathvector.yml under /etc/ with the following. Make sure to change all the IPs to match your config
asn: 215755
merge-paths: true
router-id: "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx"
prefixes:
- "2a06:9f81:3200::/48"
kernel:
learn: true
statics:
"2605:6400:ffff::2/128": "2605:6400:10::1%eth0"
templates:
upstream:
add-on-import:
- "215755:1:1"
allow-local-as: true
announce:
- "215755:1:4"
local-pref: 100
remove-all-communities: 215755
peers:
FranTech_eBGP:
asn: 53667
enforce-first-as: false
enforce-peer-nexthop: false
import-next-hop: "2605:6400:10::1"
local-pref: 100
multihop: true
neighbors:
- "2605:6400:ffff::2"
password: XXXXXXXXX
pre-import-filter: bgp_path.prepend(53667);
template: upstreamto generate the bird config, use pathvector generate. You will see the following if it generates with no errors
root@localhost:~# pathvector generate
INFO[0000] Starting Pathvector 6.3.2
INFO[0000] BIRD config validation passed
INFO[0000] Reconfiguring BIRD
INFO[0000] BIRD response (multiline): Reading configuration from /etc/bird/bird.conf
INFO[0000] Processed 1 peers in 0s To check if your prefix is announced, run the following bird command birdc s p a
You are looking to see if the connection is established at the top, then check number of routes exported at the bottom.
FRANTECH_EBGP_AS53667_v6 BGP --- up 2024-01-17 18:04:40 Established
BGP state: Established
Neighbor address: 2605:6400:ffff::2
Neighbor AS: 53667
Local AS: 215755
Neighbor ID: 169.254.169.179
Local capabilities
Multiprotocol
AF announced: ipv6
Route refresh
Graceful restart
4-octet AS numbers
Enhanced refresh
Long-lived graceful restart
Neighbor capabilities
Multiprotocol
AF announced: ipv4 ipv6
Route refresh
Graceful restart
Restart time: 120
AF supported: ipv4 ipv6
AF preserved:
4-octet AS numbers
Enhanced refresh
Long-lived graceful restart
Session: external multihop AS4
Source address: 2605:6400:10:xxxx::beef
Hold timer: 155.487/240
Keepalive timer: 12.695/80
Channel ipv6
State: UP
Table: master6
Preference: 100
Input filter: (unnamed)
Output filter: (unnamed)
Import limit: 200000
Action: disable
Routes: 0 imported, 1 exported, 0 preferred
Route change stats: received rejected filtered ignored accepted
Import updates: 0 0 0 0 0
Import withdraws: 1 0 --- 1 0
Export updates: 5 0 4 --- 1
Export withdraws: 0 --- --- --- 0
BGP Next hop: 2605:6400:10:xxxx::beef
IGP IPv6 table: master6BGP Tools check
You can also check to see if your routes are getting announced with bgp.tools